1번
class TV{
private int size;
public TV(int size) {
this.size=size;
}
protected int getSize() {
return size;
}
}
class ColorTV extends TV {
private int color;
ColorTV(int inch, int color){
super(inch);
this.color=color;
}
public void printProperty() {
System.out.print(getSize()+"인치 "+color+"컬러");
}
}
public class ex5_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ColorTV myTv=new ColorTV(65,65536);
myTv.printProperty();
}
}2번
//1번 class TV, class ColorTV 그대로 사용
class SmartTV extends ColorTV {
private String address;
SmartTV(String address,int size,int color){
super(size,color);
this.address=address;
}
public void printProperty() {
System.out.print("나의 SmartTv는 "+address+" 주소의 "+getColor()+"컬러");
}
}
public class ex5_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ColorTV myTv=new ColorTV(65,65536);
myTv.printProperty();
System.out.println();
SmartTV smartTV = new SmartTV("192.168.0.5",77,2000000);
smartTV.printProperty();
}
}3번-7번 Point 클래스 이용
class Point {
private int x,y;
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
public int getX() {return x;}
public int getY() {return y;}
protected void move (int x, int y) {
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
}3번
// toString() 메서드 재정의 (Override)
일반적으로 객체의 상태나 정보를 더 의미 있게 표현하기 위해 toString() 메서드를 재정의한다. 예를 들어, 클래스의 멤버 변수를 문자열로 반환하도록 toString() 메서드를 오버라이드할 수 있다.
class ColorPoint extends Point {
String color;
ColorPoint(int x, int y, String color){
super(x,y);
this.color=color;
}
public void setXY(int x, int y) {
move(x,y);
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color=color;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return (this.color+"색의 "+"("+this.getX()+","+this.getY()+")의 점");
}
}
public class ex5_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ColorPoint cp=new ColorPoint(5,5,"Red");
cp.setXY(10, 20);
cp.setColor("Blue");
String str = cp.toString();
System.out.println(str+"입니다.");
}
}4번
class ColorPoint2 extends Point {
String color;
ColorPoint2 (){
super(0,0);
this.color="WHITE";
}
ColorPoint2(int x,int y, String color){
super(x,y);
this.color=color;
}
ColorPoint2(int x, int y){
super(x,y);
this.color="BLACK";
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return (this.color+"색의 "+"("+this.getX()+","+this.getY()+")의 점");
}
public void set(String color) {
this.color=color;
}
public void set(int x, int y) {
move(x,y);
}
public double getDistance(ColorPoint2 point) {
return Math.sqrt((this.getX()-point.getX())*(this.getX()-point.getX())+(this.getY()-point.getY())*(this.getY()-point.getY()));
}
}
public class ex5_4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
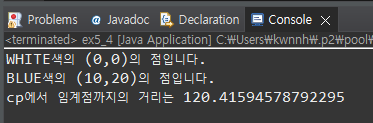
ColorPoint2 zeroPoint = new ColorPoint2();
System.out.println(zeroPoint.toString()+"입니다.");
ColorPoint2 cp= new ColorPoint2(10,10,"RED");
cp.set("BLUE");
cp.set(10,20);
System.out.println(cp.toString()+"입니다.");
ColorPoint2 thresholdPoint = new ColorPoint2(100,100);
System.out.println("cp에서 임계점까지의 거리는 "+cp.getDistance(thresholdPoint));
}
}
5번
class Point3D extends Point {
private int z;
public Point3D(int x, int y, int z) {
super(x,y);
this.z=z;
}
public void moveUp(int z) {
this.z+=z;
}
public void moveDown(int z) {
this.z-=z;
}
public void move(int x, int y, int z) {
move(x,y);
this.z=z;
}
public int getZ() {return z;}
@Override
public String toString() {
return ("("+this.getX()+","+this.getY()+","+this.getZ()+")의 점");
}
}
public class ex5_5 {
public static void main(String [] args) {
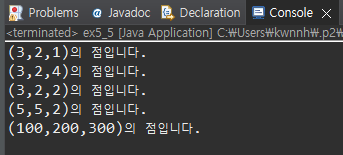
Point3D p=new Point3D(3,2,1);
System.out.println(p.toString()+"입니다.");
p.moveUp(3);
System.out.println(p.toString()+"입니다.");
p.moveDown(2);
System.out.println(p.toString()+"입니다.");
p.move(5, 5);
System.out.println(p.toString()+"입니다.");
p.move(100, 200, 300);
System.out.println(p.toString()+"입니다.");
}
}
8번
import java.util.Scanner;
abstract class Box {
protected int size;
public Box(int size) {
this.size = size;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
public abstract boolean consume();
public abstract void print();
}
class IngredientBox extends Box {
String IngredientName;
public boolean consume() {
if (!isEmpty()) {
size--;
return true;
} else {
System.out.println("원료가 부족합니다.");
return false;
}
}
public void print() {
System.out.print(size);
for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++) {
System.out.print("*");
}
}
public IngredientBox(String name, int size) {
super(size);
this.IngredientName = name;
}
}
public class ex5_8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
IngredientBox coffee = new IngredientBox("COFFEE", 5);
IngredientBox prim = new IngredientBox("PRIM", 5);
IngredientBox sugar = new IngredientBox("SUGAR", 5);
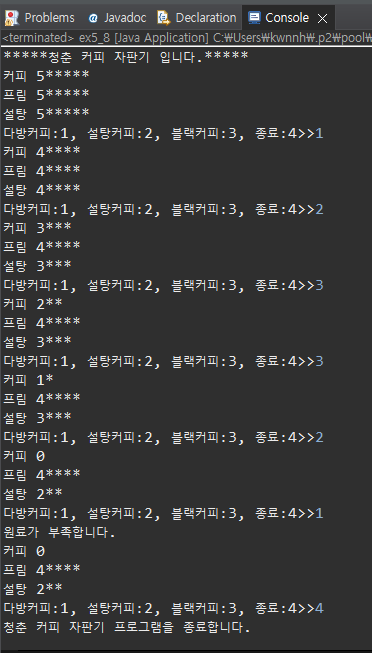
System.out.println("*****청춘 커피 자판기 입니다.*****");
int choiceMenu;
do {
System.out.print("커피 ");
coffee.print();
System.out.println();
System.out.print("프림 ");
prim.print();
System.out.println();
System.out.print("설탕 ");
sugar.print();
System.out.println();
System.out.print("다방커피:1, 설탕커피:2, 블랙커피:3, 종료:4>>");
choiceMenu = scanner.nextInt();
switch (choiceMenu) {
case 1:
if (!coffee.isEmpty() && !prim.isEmpty() && !sugar.isEmpty()) {
coffee.consume();
prim.consume();
sugar.consume();
} else {
System.out.println("원료가 부족합니다.");
}
break;
case 2:
if (!coffee.isEmpty() && !sugar.isEmpty()) {
coffee.consume();
sugar.consume();
} else {
System.out.println("원료가 부족합니다.");
}
break;
case 3:
if (!coffee.isEmpty()) {
coffee.consume();
} else {
System.out.println("원료가 부족합니다.");
}
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("청춘 커피 자판기 프로그램을 종료합니다.");
break;
default:
System.out.println("잘못된 입력입니다. 다시 시도하세요.");
break;
}
} while (choiceMenu != 4);
scanner.close();
}
}
/*
* 다방커피는 커피1 프림1 설탕1 설탕커피는 커피1 프림0 설탕1 블랙커피는 커피1 프림0 설탕0 원료가 부족하면 메시지 출력
*/
9번-10번
import java.util.Scanner;
class BaseArray {
protected int array[];
protected int nextIndex=0;
public BaseArray(int size) {
array=new int[size];
}
public int length() {return array.length;}
public void add(int n) {
if(nextIndex==array.length) {
return ;
}
array[nextIndex]=n;
nextIndex++;
}
public void print() {
for(int n: array) System.out.print(n+" ");
System.out.println();
}
}9번
class BinaryArray extends BaseArray{
int threshold;
public BinaryArray(int size, int threshold) {
super(size);
this.threshold=threshold;
}
@Override
public void add(int n) {
if(this.threshold<n) {
if(nextIndex==array.length) {
return ;
}
array[nextIndex]=1;
nextIndex++;
}
else {
if(nextIndex==array.length) {
return ;
}
array[nextIndex]=0;
nextIndex++;
}
}
}
public class ex5_9 {
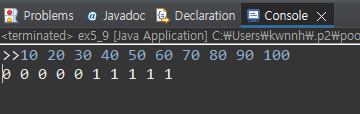
public static void main(String [] args) {
int threshold=50;
BinaryArray bArray=new BinaryArray(10,threshold);
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(">>");
for(int i=0;i<bArray.length();i++) {
int n= scanner.nextInt();
bArray.add(n);
}
bArray.print();
scanner.close();
}
}
10번
버블 정렬 알고리즘 (입력받은 배열의 원소들만 정렬하기위해 정렬의 범위(반복범위)를 nextIndex-1로 설정하였다.
for (int i = 0; i < nextIndex - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < nextIndex - 1 - i; j++) {
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
// 두 요소를 교환
int temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}class SortedArray extends BaseArray {
public SortedArray(int size) {
super(size);
}
@Override
public void add(int n) {
if(nextIndex==array.length) {
return ;
}
array[nextIndex]=n;
nextIndex++;
for (int i = 0; i < nextIndex - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < nextIndex - 1 - i; j++) {
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
// 두 요소를 교환
int temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
}
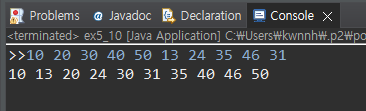
public class ex5_10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SortedArray sArray = new SortedArray(10);
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(">>");
for(int i=0;i<sArray.length();i++) {
int n=scanner.nextInt();
sArray.add(n);
}
sArray.print();
scanner.close();
}
}
11번
스택 활용
2024.08.19 - [Algorithm] - 스택(Stack) 2
스택(Stack) 2
class element { int top=-1; public static final int MAX_STACK_SIZE=100; int stack[]=new int[MAX_STACK_SIZE]; public boolean is_empty() { return (top==-1); } public boolean is_full() { return (top==(this.MAX_STACK_SIZE-1)); } public void push(int item) { if
kwone.tistory.com
import java.util.Scanner;
interface IStack{
int capacity(); //스택에 저장 가능한 개수 리턴
int length(); //스택에 현재 저장된 개수 리턴
boolean push(String item); //스택의 톱에 문자열 저장하고 true 리턴. 꽉 차서 넣을 수 없으면 false 리턴
String pop(); // 스택의 톱에 저장된 문자열 리턴. 스택이 비어 있으면 null 리턴
}
class StringStack implements IStack{
private String data[];
private int top;
private int MAX_STACK_SIZE;
public StringStack(int MAX_STACK_SIZE) {
this.top=-1;
this.MAX_STACK_SIZE=MAX_STACK_SIZE;
this.data=new String[this.MAX_STACK_SIZE];
}
@Override
public int capacity() {
return this.MAX_STACK_SIZE;
}
@Override
public int length() {
return this.top+1;
}
public boolean is_full() {
return this.top==this.MAX_STACK_SIZE-1;
}
public boolean is_empty() {
return this.top==-1;
}
@Override
public boolean push(String item) {
if(is_full()) {
System.out.printf("스택이 꽉 차서 %s 저장 불가\n",item);
return false;
}
else {
this.data[++(this.top)]=item;
return true;
}
}
@Override
public String pop() {
if(is_empty()) {
return null;
}
else {
return this.data[this.top--];
}
}
public void run() {
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
while(true) {
System.out.print("문자열 입력>>");
String str=scanner.next();
if(str.equals("그만")) {
break;
}
push(str);
}
System.out.print("스택에 저장된 문자열 팝 : ");
int n = this.length();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
System.out.print(pop()+" ");
}
scanner.close();
}
}
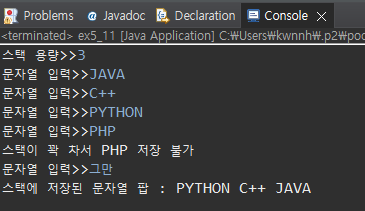
public class ex5_11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("스택 용량>>");
int size=scanner.nextInt();
StringStack ss=new StringStack(size);
ss.run();
scanner.close();
}
}
'JAVA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Money Changer with CheckBox (0) | 2024.12.06 |
|---|---|
| 컬렉션 (1) | 2024.09.24 |
| 상속 활용 예제 (0) | 2024.08.18 |
| Chapter 04 실습 문제 (0) | 2024.08.16 |
| 클래스와 객체 활용 예제 (0) | 2024.08.16 |


