#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX_DEGREE 101
typedef struct {
int degree; // 최대 차수
float x_coef[MAX_DEGREE]; // x 계수 배열
float y_coef[MAX_DEGREE]; // y 계수 배열
} polynomial;
typedef struct {
int x_exp; // x의 차수
int y_exp; // y의 차수
float coef; // 항의 계수
} term;
int compare(const void* a, const void* b) {
term* termA = (term*)a;
term* termB = (term*)b;
if (termB->y_exp != termA->y_exp) {
return termB->y_exp - termA->y_exp;
}
else {
return termB->x_exp - termA->x_exp;
}
}
void combineLikeTerms(term* resultPoly, int* term_count) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < *term_count - 1; i++) {
if (resultPoly[i].coef == 0) continue;
for (int j = i + 1; j < *term_count; j++) {
if (resultPoly[i].x_exp == resultPoly[j].x_exp && resultPoly[i].y_exp == resultPoly[j].y_exp) {
resultPoly[i].coef += resultPoly[j].coef;
resultPoly[j].coef = 0;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < *term_count; i++) {
if (resultPoly[i].coef != 0) {
resultPoly[count++] = resultPoly[i];
}
}
*term_count = count;
}
void multiPoly(polynomial a, polynomial b, term* resultPoly, int* term_count) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= a.degree; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= b.degree; j++) {
if ((a.x_coef[i] != 0 || a.y_coef[i] != 0) && (b.x_coef[j] != 0 || b.y_coef[j] != 0)) {
// x항
if (a.x_coef[i] != 0 && b.x_coef[j] != 0) {
resultPoly[count].coef = a.x_coef[i] * b.x_coef[j];
resultPoly[count].x_exp = i + j;
resultPoly[count].y_exp = 0;
count++;
}
// y항
if (a.y_coef[i] != 0 && b.y_coef[j] != 0) {
resultPoly[count].coef = a.y_coef[i] * b.y_coef[j];
resultPoly[count].x_exp = 0;
resultPoly[count].y_exp = i + j;
count++;
}
// x*y 혼합 항
if (a.x_coef[i] != 0 && b.y_coef[j] != 0) {
resultPoly[count].coef = a.x_coef[i] * b.y_coef[j];
resultPoly[count].x_exp = i;
resultPoly[count].y_exp = j;
count++;
}
if (a.y_coef[i] != 0 && b.x_coef[j] != 0) {
resultPoly[count].coef = a.y_coef[i] * b.x_coef[j];
resultPoly[count].x_exp = j;
resultPoly[count].y_exp = i;
count++;
}
}
}
}
*term_count = count;
combineLikeTerms(resultPoly, term_count);
}
void printResult(term* terms, int term_count) {
int first = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < term_count; i++) {
if (terms[i].coef == 0) continue; // 계수가 0인 항은 생략
if (!first && terms[i].coef > 0) {
printf("+");
}
if (terms[i].y_exp == 0 && terms[i].x_exp == 0) {
printf("%.1f", terms[i].coef);
}
else if (terms[i].y_exp == 0) {
printf("%.1fx^%d", terms[i].coef, terms[i].x_exp);
}
else if (terms[i].x_exp == 0) {
printf("%.1fy^%d", terms[i].coef, terms[i].y_exp);
}
else {
printf("%.1fy^%dx^%d", terms[i].coef, terms[i].y_exp, terms[i].x_exp);
}
first = 0;
}
printf("\n");
}
void initPoly(polynomial* p, const char* input) {
p->degree = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_DEGREE; i++) {
p->x_coef[i] = 0;
p->y_coef[i] = 0;
}
int sign = 1; //부호
float coef = 0;
int degree = 0;
int i = 0;
while (input[i] != '\0' && input[i] != '\n') {
if (input[i] == '+' || input[i] == '-') {
sign = (input[i] == '-') ? -1 : 1;
i++;
}
coef = 0;
while (input[i] >= '0' && input[i] <= '9') {
coef = coef * 10 + (input[i] - '0');
i++;
}
coef *= sign;
if (input[i] == 'x' || input[i] == 'y') {
char variable = input[i];
i++;
degree = 0; // 기본 차수는 0
if (input[i] == '^') {
i++;
while (input[i] >= '0' && input[i] <= '9') {
degree = degree * 10 + (input[i] - '0');
i++;
}
}
else {
degree = 1; // 기본 차수는 1
}
if (variable == 'x') {
p->x_coef[degree] += coef;
}
else if (variable == 'y') {
p->y_coef[degree] += coef;
}
if (degree > p->degree) {
p->degree = degree;
}
}
else {
p->x_coef[0] += coef;
}
}
}
int main() {
term resultPoly[MAX_DEGREE];
int term_count;
char input1[1000];
char input2[1000];
polynomial a1;
polynomial b1;
while (1) {
printf("다항식을 입력하시오: (0 입력시 종료)\n");
printf("A 다항식: ");
fgets(input1, sizeof(input1), stdin);
if (input1[0] == '0' && input1[1] == '\n') {
printf("0을 입력해서 종료합니다.\n");
break;
}
initPoly(&a1, input1);
printf("B 다항식: ");
fgets(input2, sizeof(input2), stdin);
if (input1[0] == '0' && input1[1] == '\n') {
printf("0을 입력해서 종료합니다.\n");
break;
}
initPoly(&b1, input2);
multiPoly(a1, b1, resultPoly, &term_count);
qsort(resultPoly, term_count, sizeof(term), compare);
printf("결과 다항식: ");
printResult(resultPoly, term_count);
printf("-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
}
return 0;
}다항식을 입력하시오: (0 입력시 종료)
A 다항식: 3y^7+4x^4-1
B 다항식: 5x^4-3y^2+7
결과 다항식: -9.0y^9+15.0x^4y^7+21.0y^7-12.0x^4y^2+3.0y^2+20.0x^8+23.0x^4-7.0
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
다항식을 입력하시오: (0 입력시 종료)
A 다항식: 4y^7-4x^4-1
B 다항식: 2y^7-3x+1
결과 다항식: 8.0y^14-8.0x^4y^7-12.0x^1y^7+2.0y^7+12.0x^5-4.0x^4+3.0x^1-1.0
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX_DEGREE 101
typedef struct {
int degree; // 최대 차수
float x_coef[MAX_DEGREE]; // x 계수 배열
float y_coef[MAX_DEGREE]; // y 계수 배열
} polynomial;
typedef struct {
int x_exp; // x의 차수
int y_exp; // y의 차수
float coef; // 항의 계수
} term;
int compare(const void* a, const void* b) {
term* termA = (term*)a;
term* termB = (term*)b;
if (termB->y_exp != termA->y_exp) {
return termB->y_exp - termA->y_exp;
}
else {
return termB->x_exp - termA->x_exp;
}
}
void multiPoly(polynomial a, polynomial b, term* resultPoly, int* term_count) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= a.degree; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= b.degree; j++) {
if ((a.x_coef[i] != 0 || a.y_coef[i] != 0) && (b.x_coef[j] != 0 || b.y_coef[j] != 0)) {
// x항
if (a.x_coef[i] != 0 && b.x_coef[j] != 0) {
resultPoly[count].coef = a.x_coef[i] * b.x_coef[j];
resultPoly[count].x_exp = i + j;
resultPoly[count].y_exp = 0;
count++;
}
// y항
if (a.y_coef[i] != 0 && b.y_coef[j] != 0) {
resultPoly[count].coef = a.y_coef[i] * b.y_coef[j];
resultPoly[count].x_exp = 0;
resultPoly[count].y_exp = i + j;
count++;
}
// x*y혼합 항
if (a.x_coef[i] != 0 && b.y_coef[j] != 0) {
resultPoly[count].coef = a.x_coef[i] * b.y_coef[j];
resultPoly[count].x_exp = i;
resultPoly[count].y_exp = j;
count++;
}
if (a.y_coef[i] != 0 && b.x_coef[j] != 0) {
resultPoly[count].coef = a.y_coef[i] * b.x_coef[j];
resultPoly[count].x_exp = j;
resultPoly[count].y_exp = i;
count++;
}
}
}
}
*term_count = count;
}
void printResult(term* terms, int term_count) {
int first = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < term_count; i++) {
if (terms[i].coef == 0) continue; // 계수가 0인 항은 생략
if (!first && terms[i].coef > 0) {
printf("+");
}
if (terms[i].y_exp == 0 && terms[i].x_exp == 0) {
printf("%.1f", terms[i].coef);
}
else if (terms[i].y_exp == 0) {
printf("%.1fx^%d", terms[i].coef, terms[i].x_exp);
}
else if (terms[i].x_exp == 0) {
printf("%.1fy^%d", terms[i].coef, terms[i].y_exp);
}
else {
printf("%.1fy^%dx^%d", terms[i].coef, terms[i].y_exp, terms[i].x_exp);
}
first = 0;
}
printf("\n");
}
void initPoly(polynomial* p, const char* input) {
p->degree = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_DEGREE; i++) {
p->x_coef[i] = 0;
p->y_coef[i] = 0;
}
int sign = 1; // 계수의 부호
float coef = 0; // 계수
int degree = 0; // 차수
int i = 0; // 인덱스
while (input[i] != '\0' && input[i] != '\n') {
// 부호 처리
if (input[i] == '+' || input[i] == '-') {
sign = (input[i] == '-') ? -1 : 1;
i++;
}
coef = 0;
while (input[i] >= '0' && input[i] <= '9') {
coef = coef * 10 + (input[i] - '0');
i++;
}
coef *= sign;
// 변수 처리
if (input[i] == 'x' || input[i] == 'y') {
char variable = input[i];
i++;
degree = 0; // 기본 차수는 0
if (input[i] == '^') {
i++;
while (input[i] >= '0' && input[i] <= '9') {
degree = degree * 10 + (input[i] - '0');
i++;
}
}
else {
degree = 1; // 기본 차수는 1
}
if (variable == 'x') {
p->x_coef[degree] += coef;
}
else if (variable == 'y') {
p->y_coef[degree] += coef;
}
if (degree > p->degree) {
p->degree = degree;
}
}
else {
// 상수항 처리
p->x_coef[0] += coef; // 상수항을 x 계수에 저장
}
}
}
int main() {
term resultPoly[MAX_DEGREE];
int term_count;
char input1[1000];
char input2[1000];
polynomial a1;
polynomial b1;
while (1) {
printf("다항식을 입력하시오: (0 입력시 종료)\n");
printf("A 다항식: ");
fgets(input1, sizeof(input1), stdin);
if (strcmp(input1, "0\n") == 0) {
printf("0을 입력해서 종료합니다.\n");
break;
}
initPoly(&a1, input1);
printf("B 다항식: ");
fgets(input2, sizeof(input2), stdin);
if (strcmp(input2, "0\n") == 0) {
printf("0을 입력해서 종료합니다.\n");
break;
}
initPoly(&b1, input2);
multiPoly(a1, b1, resultPoly, &term_count);
qsort(resultPoly, term_count, sizeof(term), compare);
printf("결과 다항식: ");
printResult(resultPoly, term_count);
printf("-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
}
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX_DEGREE 101
typedef struct {
int degree; // 최대 차수
float x_coef[MAX_DEGREE]; // x 계수 배열
float y_coef[MAX_DEGREE]; // y 계수 배열
} polynomial;
typedef struct {
int x_exp; // x의 차수
int y_exp; // y의 차수
float coef; // 항의 계수
} term;
int compare(const void* a, const void* b) {
term* termA = (term*)a;
term* termB = (term*)b;
if (termB->y_exp != termA->y_exp) {
return termB->y_exp - termA->y_exp;
}
else {
return termB->x_exp - termA->x_exp;
}
}
void multiPoly(polynomial a, polynomial b, term* resultPoly, int* term_count) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= a.degree; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= b.degree; j++) {
if ((a.x_coef[i] != 0 || a.y_coef[i] != 0) && (b.x_coef[j] != 0 || b.y_coef[j] != 0)) {
// x항
if (a.x_coef[i] != 0 && b.x_coef[j] != 0) {
resultPoly[count].coef = a.x_coef[i] * b.x_coef[j];
resultPoly[count].x_exp = i + j;
resultPoly[count].y_exp = 0;
count++;
}
// y항
if (a.y_coef[i] != 0 && b.y_coef[j] != 0) {
resultPoly[count].coef = a.y_coef[i] * b.y_coef[j];
resultPoly[count].x_exp = 0;
resultPoly[count].y_exp = i + j;
count++;
}
// x*y혼합 항
if (a.x_coef[i] != 0 && b.y_coef[j] != 0) {
resultPoly[count].coef = a.x_coef[i] * b.y_coef[j];
resultPoly[count].x_exp = i;
resultPoly[count].y_exp = j;
count++;
}
if (a.y_coef[i] != 0 && b.x_coef[j] != 0) {
resultPoly[count].coef = a.y_coef[i] * b.x_coef[j];
resultPoly[count].x_exp = j;
resultPoly[count].y_exp = i;
count++;
}
}
}
}
*term_count = count;
}
void printResult(term* terms, int term_count) {
int first = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < term_count; i++) {
if (terms[i].coef == 0) continue; // 계수가 0인 항은 생략
if (!first && terms[i].coef > 0) {
printf("+");
}
if (terms[i].y_exp == 0 && terms[i].x_exp == 0) {
printf("%.1f", terms[i].coef);
}
else if (terms[i].y_exp == 0) {
printf("%.1fx^%d", terms[i].coef, terms[i].x_exp);
}
else if (terms[i].x_exp == 0) {
printf("%.1fy^%d", terms[i].coef, terms[i].y_exp);
}
else {
printf("%.1fy^%dx^%d", terms[i].coef, terms[i].y_exp, terms[i].x_exp);
}
first = 0;
}
printf("\n");
}
void initPoly(polynomial* p, const char* input) {
p->degree = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_DEGREE; i++) {
p->x_coef[i] = 0;
p->y_coef[i] = 0;
}
int sign = 1; // 계수의 부호
float coef = 0; // 계수
int degree = 0; // 차수
int i = 0; // 인덱스
while (input[i] != '\0' && input[i] != '\n') {
// 부호 처리
if (input[i] == '+' || input[i] == '-') {
sign = (input[i] == '-') ? -1 : 1;
i++;
}
coef = 0;
while (input[i] >= '0' && input[i] <= '9') {
coef = coef * 10 + (input[i] - '0');
i++;
}
coef *= sign;
// 변수 처리
if (input[i] == 'x' || input[i] == 'y') {
char variable = input[i];
i++;
degree = 0; // 기본 차수는 0
if (input[i] == '^') {
i++;
while (input[i] >= '0' && input[i] <= '9') {
degree = degree * 10 + (input[i] - '0');
i++;
}
}
else {
degree = 1; // 기본 차수는 1
}
if (variable == 'x') {
p->x_coef[degree] += coef;
}
else if (variable == 'y') {
p->y_coef[degree] += coef;
}
if (degree > p->degree) {
p->degree = degree;
}
}
else {
// 상수항 처리
p->x_coef[0] += coef; // 상수항을 x 계수에 저장
}
}
}
int main() {
term resultPoly[MAX_DEGREE];
int term_count;
char input1[1000];
char input2[1000];
polynomial a1;
polynomial b1;
do {
printf("다항식을 입력하시오: (0 입력시 종료)\n");
printf("A 다항식: ");
fgets(input1, sizeof(input1), stdin);
initPoly(&a1, input1);
printf("B 다항식: ");
fgets(input2, sizeof(input2), stdin);
initPoly(&b1, input2);
multiPoly(a1, b1, resultPoly, &term_count);
qsort(resultPoly, term_count, sizeof(term), compare);
printf("결과 다항식: ");
printResult(resultPoly, term_count);
printf("-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
} while (input1 == 0||input2==0);
printf("0을 입력하여 종료합니다.");
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX_DEGREE 101
typedef struct {
int degree; // 최대 차수
float x_coef[MAX_DEGREE]; // x 계수 배열
float y_coef[MAX_DEGREE]; // y 계수 배열
} polynomial;
typedef struct {
int x_exp; // x의 차수
int y_exp; // y의 차수
float coef; // 항의 계수
} term;
int compare(const void* a, const void* b) {
term* termA = (term*)a;
term* termB = (term*)b;
if (termB->y_exp != termA->y_exp) {
return termB->y_exp - termA->y_exp;
}
else {
return termB->x_exp - termA->x_exp;
}
}
void multiPoly(polynomial a, polynomial b, term* resultPoly, int* term_count) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= a.degree; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= b.degree; j++) {
if ((a.x_coef[i] != 0 || a.y_coef[i] != 0) && (b.x_coef[j] != 0 || b.y_coef[j] != 0)) {
// x 항 곱하기
if (a.x_coef[i] != 0 && b.x_coef[j] != 0) {
resultPoly[count].coef = a.x_coef[i] * b.x_coef[j];
resultPoly[count].x_exp = a.degree - i + b.degree - j;
resultPoly[count].y_exp = 0;
count++;
}
// y 항 곱하기
if (a.y_coef[i] != 0 && b.y_coef[j] != 0) {
resultPoly[count].coef = a.y_coef[i] * b.y_coef[j];
resultPoly[count].x_exp = 0;
resultPoly[count].y_exp = a.degree - i + b.degree - j;
count++;
}
// x*y 혼합 항 곱하기
if (a.x_coef[i] != 0 && b.y_coef[j] != 0) {
resultPoly[count].coef = a.x_coef[i] * b.y_coef[j];
resultPoly[count].x_exp = a.degree - i;
resultPoly[count].y_exp = b.degree - j;
count++;
}
if (a.y_coef[i] != 0 && b.x_coef[j] != 0) {
resultPoly[count].coef = a.y_coef[i] * b.x_coef[j];
resultPoly[count].x_exp = b.degree - j;
resultPoly[count].y_exp = a.degree - i;
count++;
}
}
}
}
*term_count = count;
}
void printResult(term* terms, int term_count) {
int first = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < term_count; i++) {
if (terms[i].coef == 0) continue; // 계수가 0인 항은 생략
// 부호 출력
if (!first && terms[i].coef > 0) {
printf("+");
}
// 상수항 처리
if (terms[i].y_exp == 0 && terms[i].x_exp == 0) {
printf("%.1f", terms[i].coef); // 상수 출력
}
else if (terms[i].y_exp == 0) {
printf("%.1fx^%d", terms[i].coef, terms[i].x_exp); // y^0 생략
}
else if (terms[i].x_exp == 0) {
printf("%.1fy^%d", terms[i].coef, terms[i].y_exp); // x^0 생략
}
else {
printf("%.1fy^%dx^%d", terms[i].coef, terms[i].y_exp, terms[i].x_exp);
}
first = 0;
}
printf("\n");
}
void printPoly(polynomial poly) {
int first = 1; // 첫 번째 항 여부
for (int i = 0; i <= poly.degree; i++) {
// x 계수 출력
if (poly.x_coef[i] != 0) {
// 부호 출력
if (!first && poly.x_coef[i] > 0) {
printf("+");
}
// x^0 생략 처리
if (i == poly.degree) { // 상수항인 경우
printf("%.1f", poly.x_coef[i]); // x^0은 그냥 계수 출력
}
else {
printf("%.1fx^%d", poly.x_coef[i], poly.degree - i);
}
first = 0; // 첫 번째 항 이후
}
// y 계수 출력
if (poly.y_coef[i] != 0) {
// 부호 출력
if (!first && poly.y_coef[i] > 0) {
printf("+");
}
// y^0 생략 처리
if (i == poly.degree) { // 상수항인 경우
printf("%.1f", poly.y_coef[i]); // y^0은 그냥 계수 출력
}
else {
printf("%.1fy^%d", poly.y_coef[i], poly.degree - i);
}
first = 0; // 첫 번째 항 이후
}
}
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
term resultPoly[MAX_DEGREE];
int term_count;
polynomial a1 = { 7, {0, 0, 0, 4, 0, 0, 0, -1}, {3, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0} };
polynomial b1 = { 4, {5, 0, 0, 0, 7}, {0, 0, -3, 0, 0} };
printf("A 다항식: ");
printPoly(a1);
printf("B 다항식: ");
printPoly(b1);
multiPoly(a1, b1, resultPoly, &term_count);
qsort(resultPoly, term_count, sizeof(term), compare);
printf("결과 다항식: ");
printResult(resultPoly, term_count);
printf("-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
polynomial a2 = { 7,{0,0,0,-4,0,0,0,-1},{4,0,0,0,0,0,0,0} };
polynomial b2 = { 7,{0,0,0,0,0,0,-3,1},{2,0,0,0,0,0,0,0} };
printf("A 다항식: ");
printPoly(a2);
printf("B 다항식: ");
printPoly(b2);
multiPoly(a2, b2, resultPoly, &term_count);
qsort(resultPoly, term_count, sizeof(term), compare);
printf("결과 다항식: ");
printResult(resultPoly, term_count);
printf("-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX_DEGREE 101
typedef struct {
int degree; // 최대 차수
float x_coef[MAX_DEGREE]; // x 계수 배열
float y_coef[MAX_DEGREE]; // y 계수 배열
} extended_polynomial;
typedef struct {
int x_exp; // x의 차수
int y_exp; // y의 차수
float coef; // 항의 계수
} term;
// term 배열에서 y의 차수에 따라 내림차순 정렬
int compare(const void* a, const void* b) {
term* termA = (term*)a;
term* termB = (term*)b;
// y의 차수로 정렬하되, 동일한 경우 x 차수를 비교
if (termB->y_exp != termA->y_exp) {
return termB->y_exp - termA->y_exp;
}
else {
return termB->x_exp - termA->x_exp; // x 차수에 대해 내림차순
}
}
// 다항식 곱셈 함수
void multiply_polynomials(extended_polynomial* a, extended_polynomial* b, term* result, int* term_count) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= a->degree; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= b->degree; j++) {
if ((a->x_coef[i] != 0 || a->y_coef[i] != 0) && (b->x_coef[j] != 0 || b->y_coef[j] != 0)) {
// x 항 곱하기
if (a->x_coef[i] != 0 && b->x_coef[j] != 0) {
result[count].coef = a->x_coef[i] * b->x_coef[j];
result[count].x_exp = i + j;
result[count].y_exp = 0;
count++;
}
// y 항 곱하기
if (a->y_coef[i] != 0 && b->y_coef[j] != 0) {
result[count].coef = a->y_coef[i] * b->y_coef[j];
result[count].x_exp = 0;
result[count].y_exp = i + j;
count++;
}
// x*y 혼합 항 곱하기
if (a->x_coef[i] != 0 && b->y_coef[j] != 0) {
result[count].coef = a->x_coef[i] * b->y_coef[j];
result[count].x_exp = i;
result[count].y_exp = j;
count++;
}
if (a->y_coef[i] != 0 && b->x_coef[j] != 0) {
result[count].coef = a->y_coef[i] * b->x_coef[j];
result[count].x_exp = j;
result[count].y_exp = i;
count++;
}
}
}
}
*term_count = count;
}
// 다항식 출력 함수 (x^0이나 y^0 처리)
void print_polynomial(term* terms, int term_count) {
int first = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < term_count; i++) {
if (terms[i].coef == 0) continue; // 계수가 0인 항은 생략
// 부호 출력
if (!first && terms[i].coef > 0) {
printf("+");
}
// 상수항 처리
if (terms[i].y_exp == 0 && terms[i].x_exp == 0) {
printf("%.1f", terms[i].coef); // 상수 출력
}
else if (terms[i].y_exp == 0) {
printf("%.1fx^%d", terms[i].coef, terms[i].x_exp); // y^0 생략
}
else if (terms[i].x_exp == 0) {
printf("%.1fy^%d", terms[i].coef, terms[i].y_exp); // x^0 생략
}
else {
printf("%.1fy^%dx^%d", terms[i].coef, terms[i].y_exp, terms[i].x_exp);
}
first = 0;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
// 다항식 초기화 (test case 3)
extended_polynomial a1 = { 7, {-1, 0, 0, 0, 4, 0, 0, 0}, {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 3} };
extended_polynomial b1 = { 4, {7, 0, 0, 0, 5}, {0, 0, -3, 0, 0} };
// 결과를 저장할 배열
term result[MAX_DEGREE * MAX_DEGREE];
int term_count;
// 다항식 곱셈
multiply_polynomials(&a1, &b1, result, &term_count);
// y의 차수에 대해 내림차순 정렬
qsort(result, term_count, sizeof(term), compare);
// 결과 출력
printf("결과 다항식: ");
print_polynomial(result, term_count);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX_DEGREE 101
typedef struct {
int x_degree; //다항식의 하나의 항에서의 x의 차수
int y_degree; //다항식의 하나의 항에서의 y의 차수
int coef; //다항식의 하나의 항에서의 계수
}term; //다항식중에서 하나의 항을 나타내는 구조체
typedef struct {
term terms[MAX_DEGREE]; //다항식의 항 별 요소(term 구조체 배열 : x의 차수,y의 차수,계수)
int terms_count; //다항식의 전체 항 개수
}polynomial; //다항식은 여러 항으로 구성되어 있으므로 각 항들의 요소(x,y의 차수,항 별 계수)와 전체 항의 개수를 포함하는 구조체
int compare(const void* a, const void* b) {
term* termA = (term*)a;
term* termB = (term*)b;
if (termA->y_degree != termB->y_degree) {
return termB->y_degree - termA->y_degree;
}
else {
return termB->x_degree - termA->x_degree;
}
}
polynomial mult_Poly(polynomial a, polynomial b)
{
polynomial c;
c.terms_count = 0; //항의 개수 0으로 초기화
//각 항별 곱셈 진행
for (int i = 0; i < a.terms_count; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < b.terms_count; j++) {
term temp_term;
temp_term.coef = a.terms[i].coef * b.terms[j].coef;
temp_term.x_degree = a.terms[i].x_degree + b.terms[j].x_degree;
temp_term.y_degree = a.terms[i].y_degree + b.terms[j].y_degree;
c.terms[c.terms_count++] = temp_term;
}
}
//차수가 같은 항 계수 정리
for (int i = 0; i < c.terms_count; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < c.terms_count; j++) {
if (c.terms[i].x_degree == c.terms[j].x_degree && c.terms[i].y_degree == c.terms[j].y_degree) {
c.terms[i].coef += c.terms[j].coef;
//j번째 항 삭제 (한칸 앞으로 밀어 덮어씌움)
for (int k = j; k < c.terms_count - 1; k++) {
c.terms[k] = c.terms[k + 1];
}
c.terms_count--;
j--;
}
}
}
qsort(c.terms, c.terms_count, sizeof(term), compare);
return c;
}
void print_Poly(polynomial p)
{
for (int i = 0; i < p.terms_count; i++) {
if (p.terms[i].coef != 0) {
if (p.terms[i].coef > 0) { printf("+"); }
printf("%d", p.terms[i].coef);
if (p.terms[i].y_degree > 0) {
printf("y^%d",p.terms[i].y_degree);
}
if (p.terms[i].x_degree > 0) {
printf("x^%d", p.terms[i].x_degree);
}
}
}
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
polynomial a1 = { { {0, 7, 3}, {4, 0, 4}, {0, 0, -1} }, 3 };
polynomial b1 = { { {4, 0, 5}, {0, 2, -3}, {0, 0, 7} }, 3 };
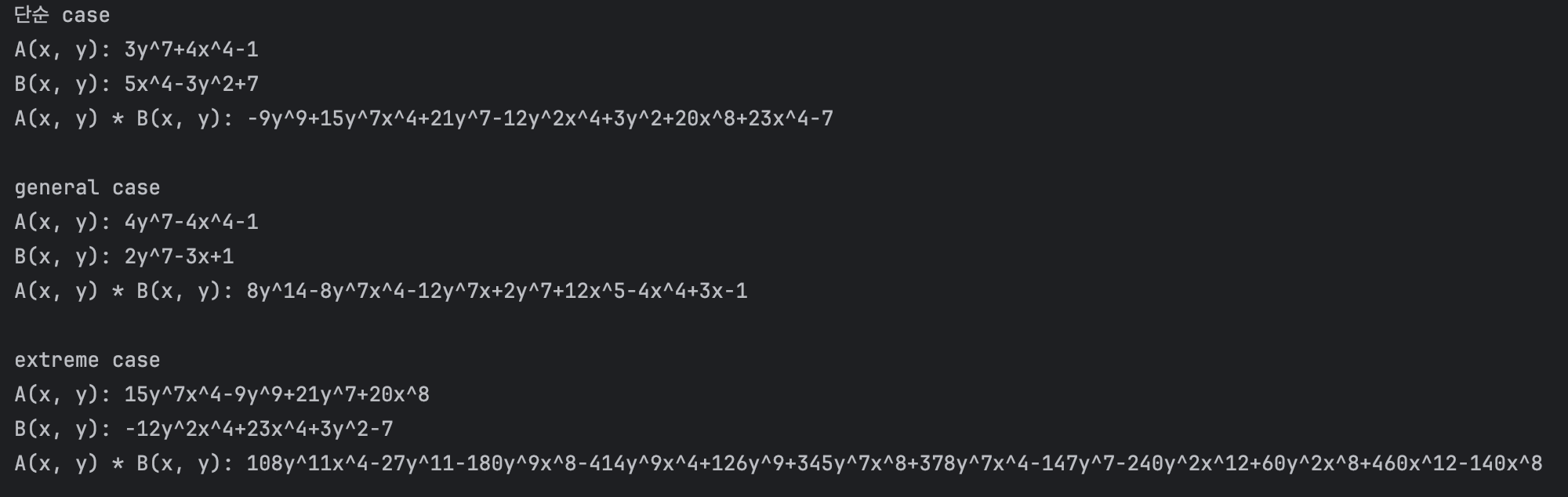
printf("단순 case\n");
print_Poly(a1);
print_Poly(b1);
printf("-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
polynomial result1 = mult_Poly(a1, b1);
print_Poly(result1);
polynomial a2 = { { {0, 7, 4}, {4, 0, -4}, {0, 0, -1} }, 3 };
polynomial b2 = { { {0, 7, 2}, {1, 0, -3}, {0, 0, 1} }, 3 };
printf("\ngeneral case\n");
print_Poly(a2);
print_Poly(b2);
printf("-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
polynomial result2 = mult_Poly(a2, b2);
print_Poly(result2);
polynomial a3 = { { {4, 7, 15}, {0, 9, -9}, {0, 7, 21}, {8, 0, 20} }, 4 };
polynomial b3 = { { {4, 2, -12}, {4, 0, 23}, {0, 2, 3}, {0, 0, -7} }, 4 };
printf("\nextreme case\n");
print_Poly(a3);
print_Poly(b3);
printf("-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
polynomial result3 = mult_Poly(a3, b3);
print_Poly(result3);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX_DEGREE 101
#define MAX(a,b) (((a)>(b))?(a):(b))
typedef struct {
int x_exp; // x의 차수
int y_exp; // y의 차수
int coef; // 계수 (정수로 변경)
} term;
typedef struct {
term terms[MAX_DEGREE];
int term_count; //곱셈을 위한 항의개수
} polynomial;
// 비교 함수: y 차수를 기준으로 내림차순 정렬, y 차수가 같으면 x 차수 내림차순
int compare(const void* a, const void* b) {
term* term_a = (term*)a;
term* term_b = (term*)b;
if (term_a->y_exp != term_b->y_exp)
return term_b->y_exp - term_a->y_exp; // y 차수에 대해 내림차순
return term_b->x_exp - term_a->x_exp; // y 차수가 같으면 x 차수에 대해 내림차순
}
// 다항식의 곱 함수
polynomial multPoly(polynomial a, polynomial b) {
polynomial c;
c.term_count = 0;
// 각 항을 곱함
for (int i = 0; i < a.term_count; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < b.term_count; j++) {
term new_term; //새로운항을 만들고 한번 곱셈하여 저장함
new_term.coef = a.terms[i].coef * b.terms[j].coef;
new_term.x_exp = a.terms[i].x_exp + b.terms[j].x_exp;
new_term.y_exp = a.terms[i].y_exp + b.terms[j].y_exp;
// 동일한 차수가 있으면 계수를 합산
int found = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < c.term_count; k++) {
if (c.terms[k].x_exp == new_term.x_exp && c.terms[k].y_exp == new_term.y_exp) {
c.terms[k].coef += new_term.coef;
found = 1;
break;
}
}
if (!found) {
c.terms[c.term_count++] = new_term;
}
}
}
// qsort를 이용하여 y 차수를 기준으로 내림차순 정렬
qsort(c.terms, c.term_count, sizeof(term), compare);
return c;
}
// 다항식 출력 함수
void printPoly(polynomial p) {
for (int i = 0; i < p.term_count; i++) {
if (p.terms[i].coef != 0) {
if (i > 0 && p.terms[i].coef > 0) printf("+");
printf("%d", p.terms[i].coef); // 계수를 정수로 출력
if (p.terms[i].y_exp > 0) {
printf("y");
if (p.terms[i].y_exp > 1) printf("^%d", p.terms[i].y_exp);
}
if (p.terms[i].x_exp > 0) {
printf("x");
if (p.terms[i].x_exp > 1) printf("^%d", p.terms[i].x_exp);
}
}
}
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
// 단순 case
polynomial a1 = {{ {0, 7, 3}, {4, 0, 4}, {0, 0, -1} }, 3}; // 3y^7 + 4x^4 - 1
polynomial b1 = {{ {4, 0, 5}, {0, 2, -3}, {0, 0, 7} }, 3}; // 5x^4 - 3y^2 + 7
printf("단순 case\nA(x, y): ");
printPoly(a1);
printf("B(x, y): ");
printPoly(b1);
polynomial result1 = multPoly(a1, b1);
printf("A(x, y) * B(x, y): ");
printPoly(result1);
// general case
polynomial a2 = {{ {0, 7, 4}, {4, 0, -4}, {0, 0, -1} }, 3}; // 4y^7 - 4x^4 - 1
polynomial b2 = {{ {0, 7, 2}, {1, 0, -3}, {0, 0, 1} }, 3}; // 2y^7 - 3x + 1
printf("\ngeneral case\nA(x, y): ");
printPoly(a2);
printf("B(x, y): ");
printPoly(b2);
polynomial result2 = multPoly(a2, b2);
printf("A(x, y) * B(x, y): ");
printPoly(result2);
// extreme case
polynomial a3 = {{ {4, 7, 15}, {0, 9, -9}, {0, 7, 21}, {8, 0, 20} }, 4}; // 15x^4y^7 -9y^9 +21y^7 +20x^8
polynomial b3 = {{ {4, 2, -12}, {4, 0, 23}, {0, 2, 3}, {0, 0, -7} }, 4}; // -12x^4y^2 +23x^4 +3y^2 -7
printf("\nextreme case\nA(x, y): ");
printPoly(a3);
printf("B(x, y): ");
printPoly(b3);
polynomial result3 = multPoly(a3, b3);
printf("A(x, y) * B(x, y): ");
printPoly(result3);
return 0;
}다항식 곱셈기
polynomial poly_add1(polynomial a,polynomial b) {
polynomial c;
int Apos=0,Bpos=0,Cpos=0;
int degree_a=a.degree,degree_b=b.degree;
c.degree=MAX(a.degree,b.degree);
while(Apos<=degree_a && Bpos<=degree_b) {
if(degree_a>degree_b) {
//A항>B항
c.coef[Cpos++]=a.coef[Apos++]; //c다항식에
degree_a--;
}
else if(degree_b==degree_a) {
c.coef[Cpos++]=b.coef[Bpos++];
degree_b--;
degree_a--;
}
else {
c.coef[Cpos++]=b.coef[Bpos++];
degree_b--;
}
}
return c;
}
다항식 덧셈기
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX_DEGREE 101
#define MAX(a,b) (((a)>(b))?(a):(b))
typedef struct {
int degree;
float coef[MAX_DEGREE];
}polynomial;
polynomial poly_subtract (polynomial a,polynomial b) {
polynomial result;
int Apos=0,Bpos=0,Cpos=0;
int degree_a=a.degree;
int degree_b=b.degree;
result.degree=MAX(a.degree,b.degree);
while(Apos<=a.degree&&Bpos<=b.degree) {
if(degree_a>degree_b) {
result.coef[Cpos++]=a.coef[Apos++];
degree_a--;
}
else if(degree_a==degree_b) {
result.coef[Cpos++]=a.coef[Apos++]-b.coef[Bpos++];
degree_a--,degree_b--;
}
else {
result.coef[Cpos++]=b.coef[Bpos++];
degree_b--;
}
}
return result;
}
void print_poly(polynomial p) {
for(int i=p.degree;i>0;i--) {
printf("%3.1fx^%d + ",p.coef[p.degree-i],i);
}
printf("%3.1f \n",p.coef[p.degree]);
}
int main(void){
polynomial a={5,{3,6,0,0,0,10}};
polynomial b={4,{7,0,5,0,1}};
polynomial c;
print_poly(a);
print_poly(b);
c=poly_subtract(a,b);
printf("-------------------------------------------------------------\n\n");
print_poly(c);
return 0;
}
다항식 뺄셈기
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNGINS
#define MAX 101
//두 다항식 입력받고 배열에 저장 (계수따로 지수따로)//
//최대지수는 100으로 한정, 계수와 변수사이는 *없이 그냥 입력받으며 지수의경우 ^으로 구분//
//두 다항식간의 사칙연산 함수 입력//
//다항식은 내림차순으로 입력//
//변수 이름에 한글을 쓸 시 에러가 발생하기에, 영어로 작성//
//1. subTerm = 다항식 - 다항식//
//2. addTerm = 다항식 + 다항식//
//3. delTerm = 입력했던 다항식 초기화//
//4. MultPoly = 다항식 × 다항식//
//5. exit = 종료//
typedef struct {
int expo; //최대 지수값
int coef[MAX]; //최대지수 101로 한정
}poly;
void show(poly A) // 해당 다항식 출력
{
for (int i = 0; i<A.expo; i++) {
if (A.coef[i] != 0)
printf("%dx^%d", A.coef[i], A.expo - i);
if (A.coef[i + 1] >= 0 && A.coef[i] != 0)
printf(" + ");
}
printf("%d ", A.coef[A.expo]);
}
poly polynomialSave()
{
poly C;
memset(&C, 0, sizeof(C));
int num1, num2;
printf("최고차항을 입력해주세요.\n");
scanf("%d", &num1);
C.expo = num1;
for (int i = 0; i <= num1; i++)
{
printf("x^%d의 계수를 입력해주세요.\n", num1 - i);
scanf("%d", &num2);
C.coef[i] = num2;
}
return C;
}
poly subPoly(poly A)
{
poly B;
B = polynomialSave();
poly C;
int indxA = 0, indxB = 0, indxC = 0, degA = A.expo, degB = B.expo;
C.expo = (A.expo>B.expo) ? A.expo : B.expo;//최고차항 저장
while (A.expo >= indxA && B.expo >= indxB)//각 항의 최고차항을 이용해 연산
{
if (degA == degB)
{
C.coef[indxC++] = A.coef[indxA++] - B.coef[indxB++];
degA--; degB--;
}
else if (degA>degB)
{
C.coef[indxC++] = A.coef[indxA++];
degA--;
}
else
{
C.coef[indxC++] = B.coef[indxB++];
degB--;
}
}
printf(" ");
show(A);
printf("\n %c ", '-');
show(B);
printf("\n = ");
show(C);
printf("\n");
return C;
}
poly addPoly(poly A)
{
poly B;
B = polynomialSave();
poly C;
int indxA = 0, indxB = 0, indxC = 0, degA = A.expo, degB = B.expo;
C.expo = (A.expo>B.expo) ? A.expo : B.expo;//최고차항 저장
while (A.expo >= indxA && B.expo >= indxB)// 각항의 최고차항을 이용해 연산
{
if (degA == degB)
{
C.coef[indxC++] = A.coef[indxA++] + B.coef[indxB++];
degA--; degB--;
}
else if (degA>degB)
{
C.coef[indxC++] = A.coef[indxA++];
degA--;
}
else
{
C.coef[indxC++] = B.coef[indxB++];
degB--;
}
}
printf(" ");
show(A);
printf("\n %c ", '+');
show(B);
printf("\n = ");
show(C);
printf("\n");
return C;
}
poly delTerm(poly A)
{
printf("다항식값을 초기화합니다.\n");
memset(&A, 0, sizeof(A));
return A;
}
poly MultPoly(poly A)
{
poly B;
B = polynomialSave();
poly C;
memset(&C, 0, sizeof(C));
int indxA = 0, indxB = 0, indxC = 0, degA = A.expo, degB = B.expo;
C.expo = A.expo + B.expo;//최고차항은 A,B의 최고차항의 합이다.
for (int i = 0; i <= A.expo; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j <= B.expo; j++)
{
C.coef[i + j] += A.coef[i] * B.coef[j];
}
}
printf(" ");
show(A);
printf("\n %c ", '*');
show(B);
printf("\n = ");
show(C);
printf("\n");
return C;
}
void menu(poly A)
{
int num = 0;
while (1)
{
printf("1.SubPoly 2.AddPoly 3.DelTerm 4.MultPoly 5.Exit \n");
scanf("%d", &num);
if (num == 6)
break;
switch (num)
{
case 1:
A = subPoly(A);
break;
case 2:
A = addPoly(A);
break;
case 3:
delTerm(A);
A = polynomialSave();
break;
case 4:
MultPoly(A);
break;
default:
printf("정확한 값을 넣어주세요.\n");
}
puts("");
}
}
int main()
{
poly A;
A = polynomialSave();
menu(A);
printf("프로그램을 종료합니다.\n");
return 0;
}
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| #include <stdio.h> | |
| #include <stdlib.h> | |
| #include <string.h> | |
| #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNGINS | |
| #define MAX 101 | |
| //두 다항식 입력받고 배열에 저장 (계수따로 지수따로)// | |
| //최대지수는 100으로 한정, 계수와 변수사이는 *없이 그냥 입력받으며 지수의경우 ^으로 구분// | |
| //두 다항식간의 사칙연산 함수 입력// | |
| //다항식은 내림차순으로 입력// | |
| //변수 이름에 한글을 쓸 시 에러가 발생하기에, 영어로 작성// | |
| //1. subTerm = 다항식 - 다항식// | |
| //2. addTerm = 다항식 + 다항식// | |
| //3. delTerm = 입력했던 다항식 초기화// | |
| //4. MultPoly = 다항식 × 다항식// | |
| //5. exit = 종료// | |
| typedef struct { | |
| int expo; //최대 지수값 | |
| int coef[MAX]; //최대지수 101로 한정 | |
| }poly; | |
| void show(poly A) // 해당 다항식 출력 | |
| { | |
| for (int i = 0; i<A.expo; i++) { | |
| if (A.coef[i] != 0) | |
| printf("%dx^%d", A.coef[i], A.expo - i); | |
| if (A.coef[i + 1] >= 0 && A.coef[i] != 0) | |
| printf(" + "); | |
| } | |
| printf("%d ", A.coef[A.expo]); | |
| } | |
| poly polynomialSave() | |
| { | |
| poly C; | |
| memset(&C, 0, sizeof(C)); | |
| int num1, num2; | |
| printf("최고차항을 입력해주세요.\n"); | |
| scanf("%d", &num1); | |
| C.expo = num1; | |
| for (int i = 0; i <= num1; i++) | |
| { | |
| printf("x^%d의 계수를 입력해주세요.\n", num1 - i); | |
| scanf("%d", &num2); | |
| C.coef[i] = num2; | |
| } | |
| return C; | |
| } | |
| poly subPoly(poly A) | |
| { | |
| poly B; | |
| B = polynomialSave(); | |
| poly C; | |
| int indxA = 0, indxB = 0, indxC = 0, degA = A.expo, degB = B.expo; | |
| C.expo = (A.expo>B.expo) ? A.expo : B.expo;//최고차항 저장 | |
| while (A.expo >= indxA && B.expo >= indxB)//각 항의 최고차항을 이용해 연산 | |
| { | |
| if (degA == degB) | |
| { | |
| C.coef[indxC++] = A.coef[indxA++] - B.coef[indxB++]; | |
| degA--; degB--; | |
| } | |
| else if (degA>degB) | |
| { | |
| C.coef[indxC++] = A.coef[indxA++]; | |
| degA--; | |
| } | |
| else | |
| { | |
| C.coef[indxC++] = B.coef[indxB++]; | |
| degB--; | |
| } | |
| } | |
| printf(" "); | |
| show(A); | |
| printf("\n %c ", '-'); | |
| show(B); | |
| printf("\n = "); | |
| show(C); | |
| printf("\n"); | |
| return C; | |
| } | |
| poly addPoly(poly A) | |
| { | |
| poly B; | |
| B = polynomialSave(); | |
| poly C; | |
| int indxA = 0, indxB = 0, indxC = 0, degA = A.expo, degB = B.expo; | |
| C.expo = (A.expo>B.expo) ? A.expo : B.expo;//최고차항 저장 | |
| while (A.expo >= indxA && B.expo >= indxB)// 각항의 최고차항을 이용해 연산 | |
| { | |
| if (degA == degB) | |
| { | |
| C.coef[indxC++] = A.coef[indxA++] + B.coef[indxB++]; | |
| degA--; degB--; | |
| } | |
| else if (degA>degB) | |
| { | |
| C.coef[indxC++] = A.coef[indxA++]; | |
| degA--; | |
| } | |
| else | |
| { | |
| C.coef[indxC++] = B.coef[indxB++]; | |
| degB--; | |
| } | |
| } | |
| printf(" "); | |
| show(A); | |
| printf("\n %c ", '+'); | |
| show(B); | |
| printf("\n = "); | |
| show(C); | |
| printf("\n"); | |
| return C; | |
| } | |
| poly delTerm(poly A) | |
| { | |
| printf("다항식값을 초기화합니다.\n"); | |
| memset(&A, 0, sizeof(A)); | |
| return A; | |
| } | |
| poly MultPoly(poly A) | |
| { | |
| poly B; | |
| B = polynomialSave(); | |
| poly C; | |
| memset(&C, 0, sizeof(C)); | |
| int indxA = 0, indxB = 0, indxC = 0, degA = A.expo, degB = B.expo; | |
| C.expo = A.expo + B.expo;//최고차항은 A,B의 최고차항의 합이다. | |
| for (int i = 0; i <= A.expo; i++) | |
| { | |
| for (int j = 0; j <= B.expo; j++) | |
| { | |
| C.coef[i + j] += A.coef[i] * B.coef[j]; | |
| } | |
| } | |
| printf(" "); | |
| show(A); | |
| printf("\n %c ", '*'); | |
| show(B); | |
| printf("\n = "); | |
| show(C); | |
| printf("\n"); | |
| return C; | |
| } | |
| void menu(poly A) | |
| { | |
| int num = 0; | |
| while (1) | |
| { | |
| printf("1.SubPoly 2.AddPoly 3.DelTerm 4.MultPoly 5.Exit \n"); | |
| scanf("%d", &num); | |
| if (num == 6) | |
| break; | |
| switch (num) | |
| { | |
| case 1: | |
| A = subPoly(A); | |
| break; | |
| case 2: | |
| A = addPoly(A); | |
| break; | |
| case 3: | |
| delTerm(A); | |
| A = polynomialSave(); | |
| break; | |
| case 4: | |
| MultPoly(A); | |
| break; | |
| default: | |
| printf("정확한 값을 넣어주세요.\n"); | |
| } | |
| puts(""); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| int main() | |
| { | |
| poly A; | |
| A = polynomialSave(); | |
| menu(A); | |
| printf("프로그램을 종료합니다.\n"); | |
| return 0; | |
| } |
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX_TERMS 100 /* 항 배열의 크기*/
typedef struct {
float coef;
int expon;
} polynomial;
polynomial terms[MAX_TERMS];
int avail = 0;
void attach(float coefficient, int exponent)
{ /* 새로운 항을 다항식에 첨가한다. */
if (avail >= MAX_TERMS) {
printf(" 다항식에 항이 너무 많다.");
exit(1);
}
terms[avail].coef = coefficient;
terms[avail++].expon = exponent;
}
void attach2(float coefficient, int exponent, int s) //같은 지수의 계수 더하기
{
/* 곱셈한 항을 다항식에 첨가 */
int i;
int j;
if (avail >= MAX_TERMS) {
printf("다항식에 항이 너무 많다.");
exit(1);
}
avail--;
i = avail;
for (j = i; j >= s; j--)
{
if (terms[j].expon == exponent) //지수가 같을 경우 계수를 더해줌
{
terms[j].coef += coefficient;
avail++;
return;
}
else
break;
//지수가 같지 않을 경우 그냥 다항식에 첨가
}
avail++;
terms[avail].coef = coefficient;
terms[avail++].expon = exponent;
}
void print(int start, int finish)
{
int i;
printf("\n");
if (start <= finish) {
for (i = start; i < finish; i++)
printf("%3.1f x^ %d + ", terms[i].coef, terms[i].expon);
// 마지막 항을 출력
printf("%3.1f x^ %d \n", terms[finish].coef, terms[finish].expon);
}
else
printf(" No terms ");
}
void pmult(int starta, int finisha, int startb, int finishb, int* startd, int* finishd)
{ /* A(x)와 B(x)를 곱하여 D(x)를 생성한다. */
float coefficient;
int exponent;
int i, j;
int s;
*startd = avail;
for (i = starta; i <= finisha; i++)
{
for (j = startb; j <= finishb; j++)
{
coefficient = terms[i].coef * terms[j].coef; //계수의 곱
exponent = terms[i].expon + terms[j].expon; // 지수의 합
s = finisha + finishb; // s의 위치 지정
attach2(coefficient, exponent, s); //곱셈항 첨가
}
}
*finishd = avail - 1;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int startA, finishA; // 다항식 A
int startB, finishB; // 다항식 B
int startC, finishC; // 다항식 C
int i, n, e;
float c;
printf("다항식의 곱셈 연산 수행!\n");
printf("다항식 A의 항의 수 : ");
scanf("%d", &n);
startA = avail;
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
printf("\n다항식 A의 %d 번째 항의 계수와 지수 : ", i);
scanf("%f%d", &c, &e);
attach(c, e);
}
finishA = avail - 1;
print(startA, finishA); // 다항식 A의 입력결과
printf("\n다항식 B의 항의 수 : ");
scanf("%d", &n);
startB = avail;
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
printf("\n다항식 B의 %d 번째 항의 계수와 지수 : ", i);
scanf("%f%d", &c, &e);
attach(c, e);
}
finishB = avail - 1;
print(startB, finishB); // 다항식 b의 입력결과
pmult(startA, finishA, startB, finishB, &startC, &finishC); // 곱셈
printf(" \n 곱셈의 결과 : ");
print(startC, finishC); // 곱셈 결과 출력
return 0;
}'DSA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 회문(Palindrome) 검사 (스택) (1) | 2024.10.27 |
|---|---|
| 스택 2개를 이용한 선형 큐의 구현 (0) | 2024.10.25 |
| 리스트 1 (ArrayList) (0) | 2024.08.26 |
| 큐(Queue) 활용 예제 (0) | 2024.08.26 |
| 덱(Deque) 2 (0) | 2024.08.25 |



